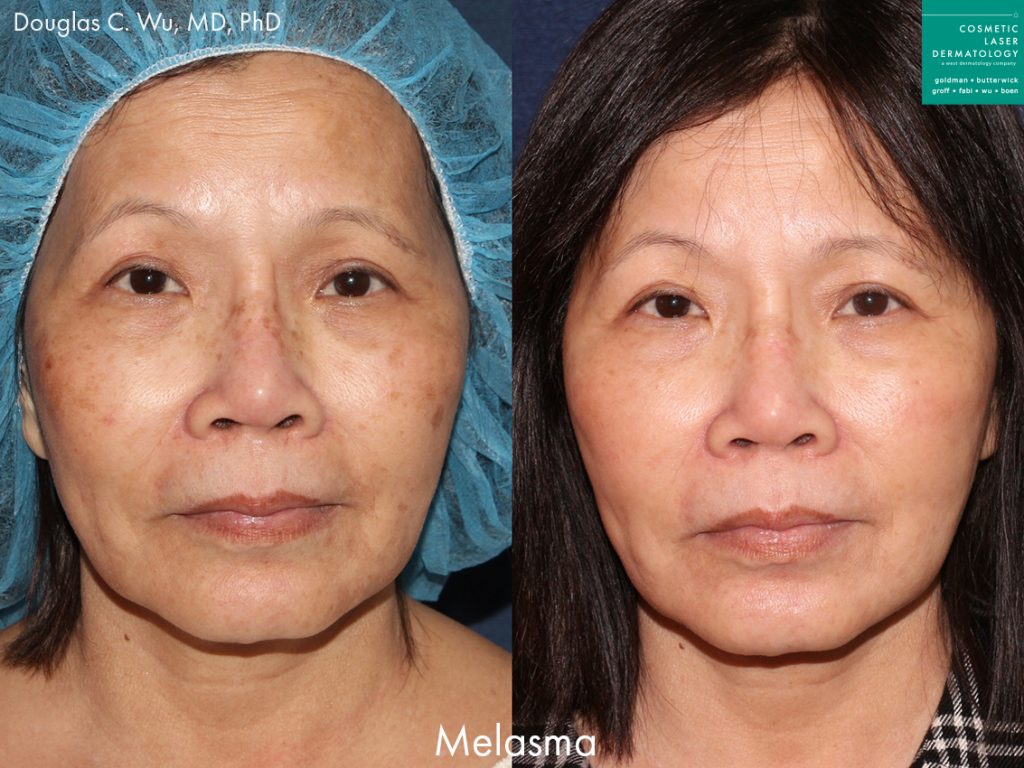
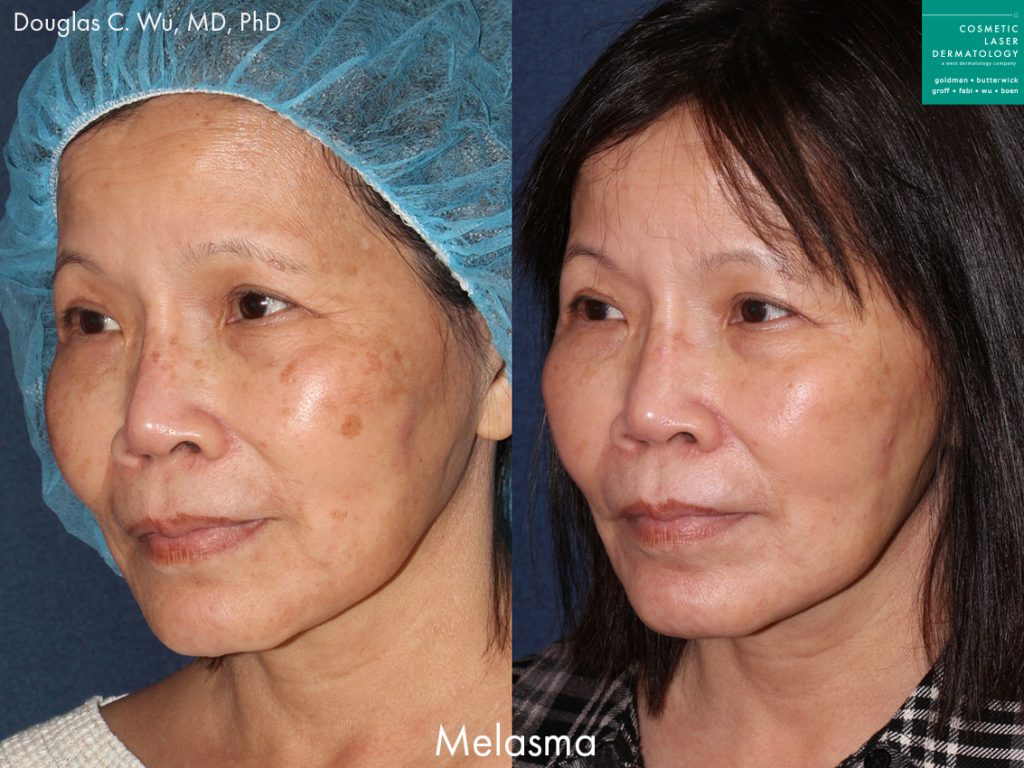
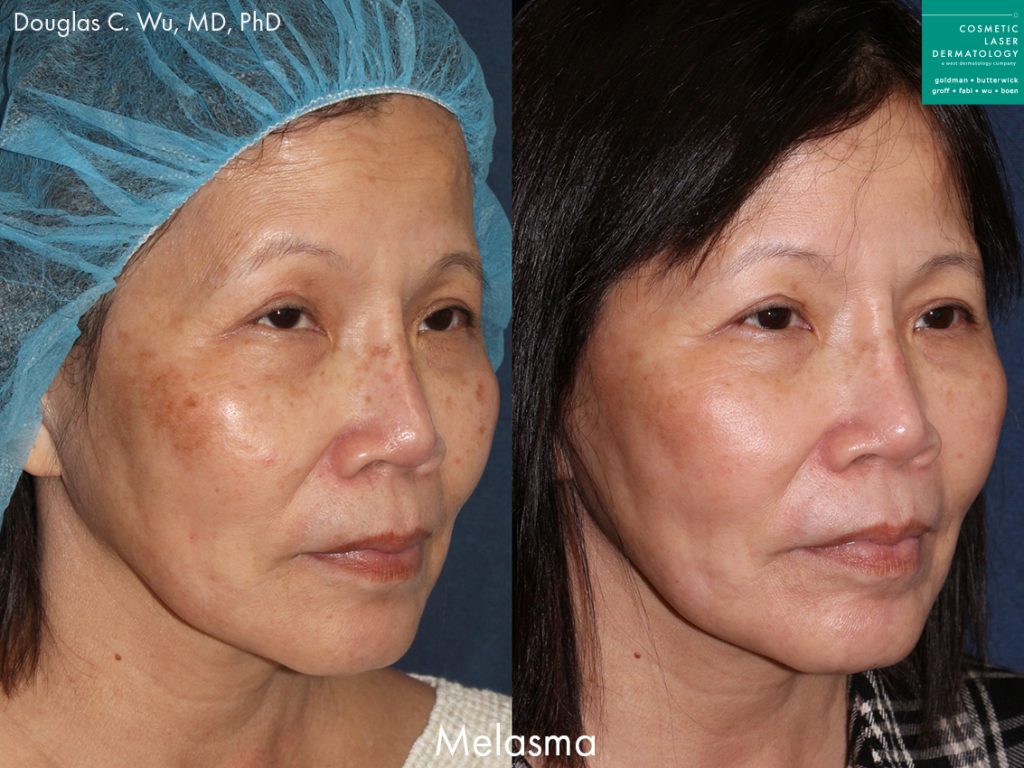
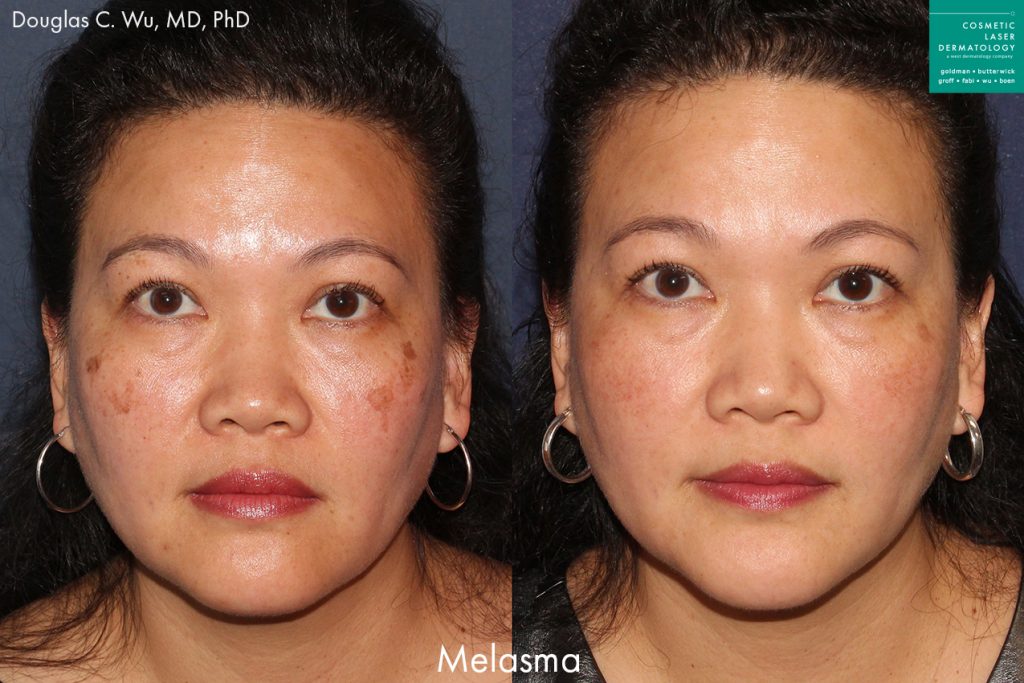
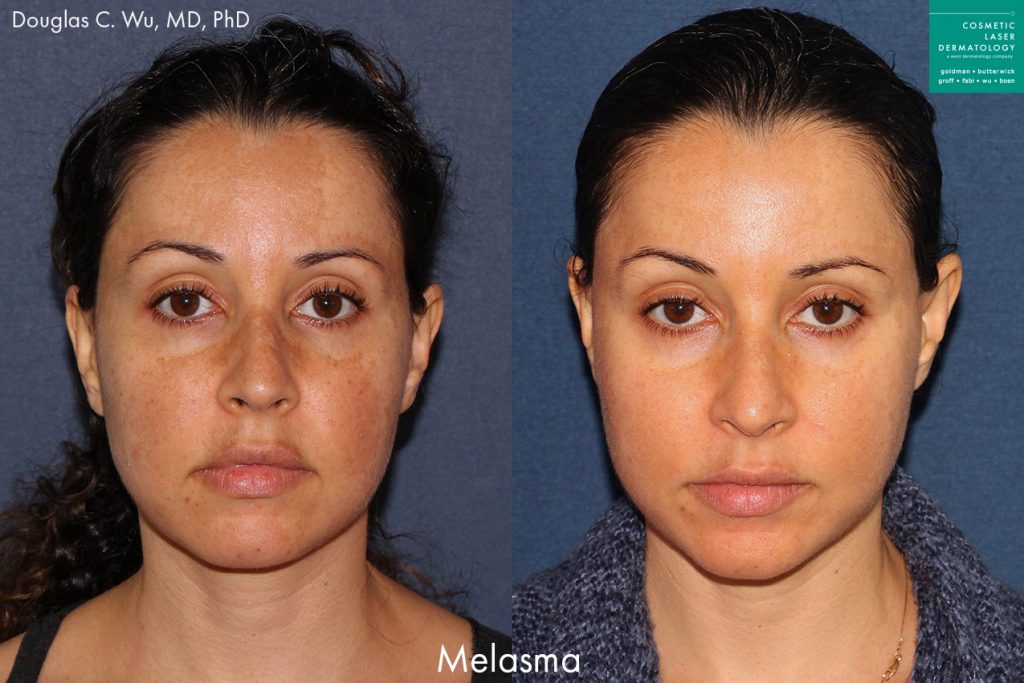
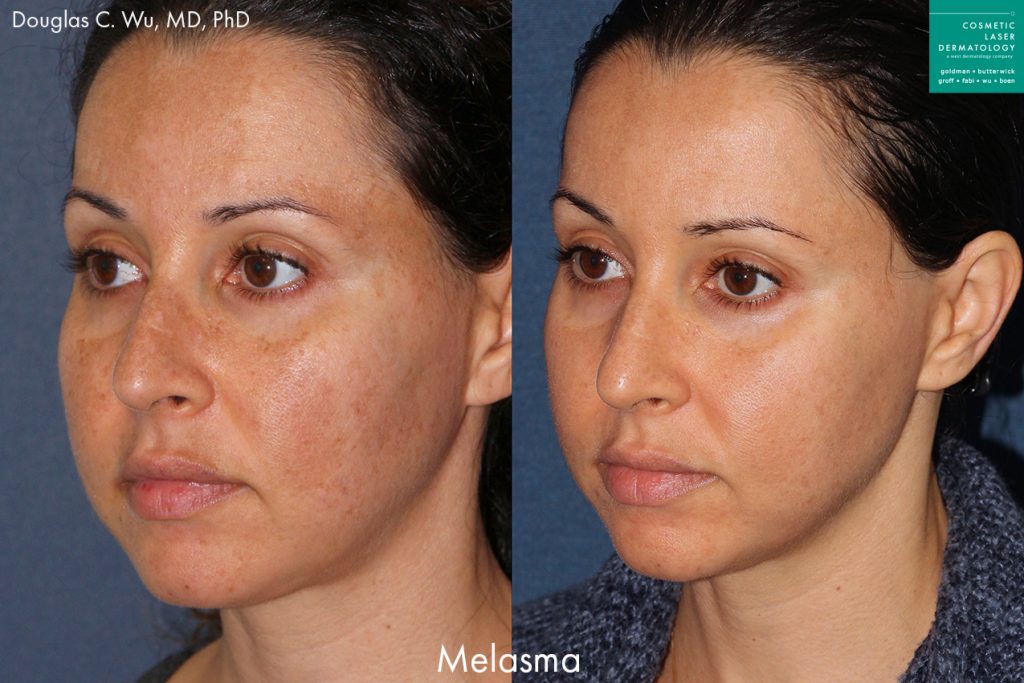
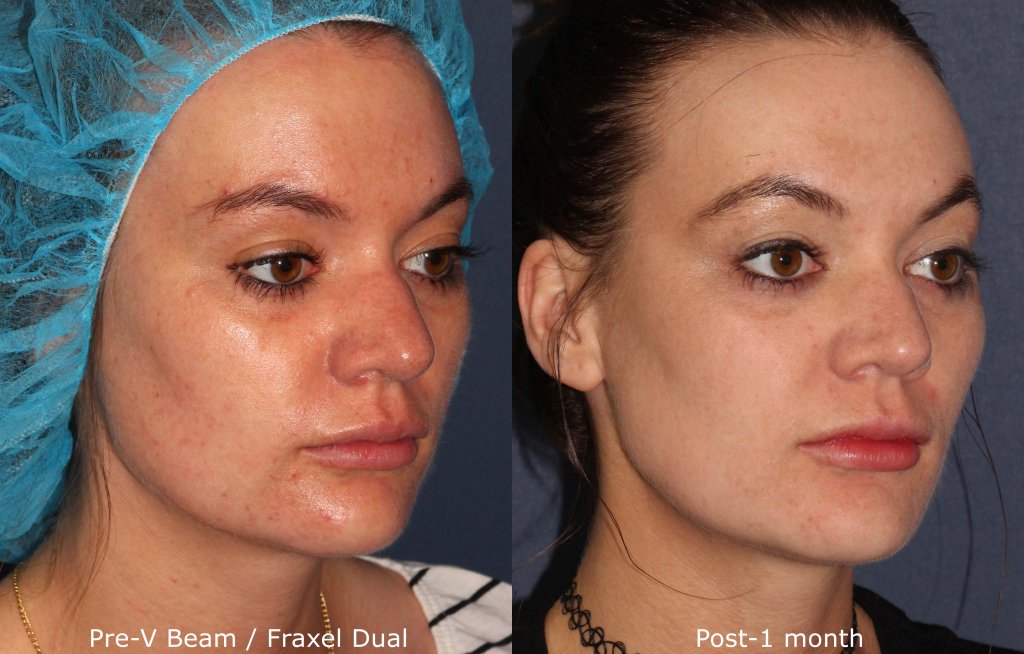
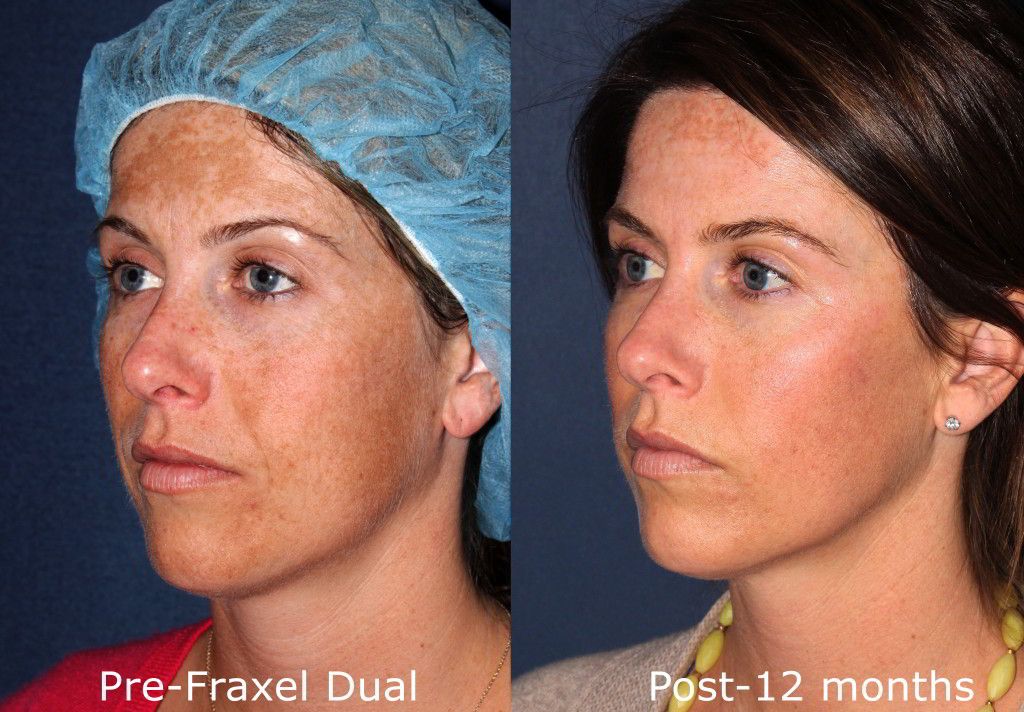
Melasma Overview
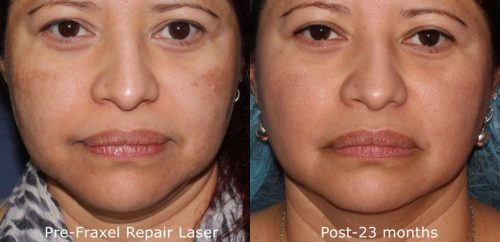
Also known as chloasma, melasma is a fairly common dermatological condition that causes hyperpigmentation, resulting in brown and tan spots and discolorations of the skin. The condition can technically affect people of all ages but is most common in adulthood. The most common causes are sun exposure, and the hormonal fluctuations associated with pregnancy, making it more common in women. In some cases, melasma may fade on its own, others may require treatment.
Signs and Symptoms of Melasma
The spots and discoloration usually develop on the face, particularly on the chin, nose, cheeks, and forehead. People with melasma typically notice darkened brown or gray patches on their skin. Melasma can also develop on other parts of the body that receive frequent sun exposure, like the neck, arms, and hands. Because the condition is especially common among pregnant women, it is also referred to as the pregnancy mask.
Prolonged sun exposure can also increase the risk of developing facial patches and other forms of skin cancer. The dermatologists at San Diego-based Cosmetic Laser Dermatology suggest scheduling an appointment at the first sign of new growths or spots and discolorations of the skin.
Treatment Options
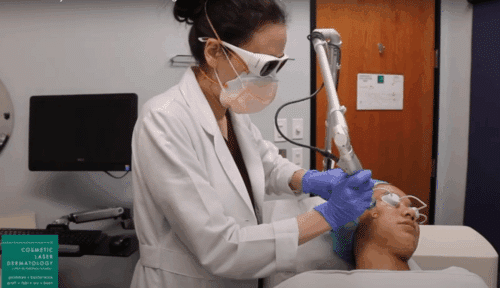
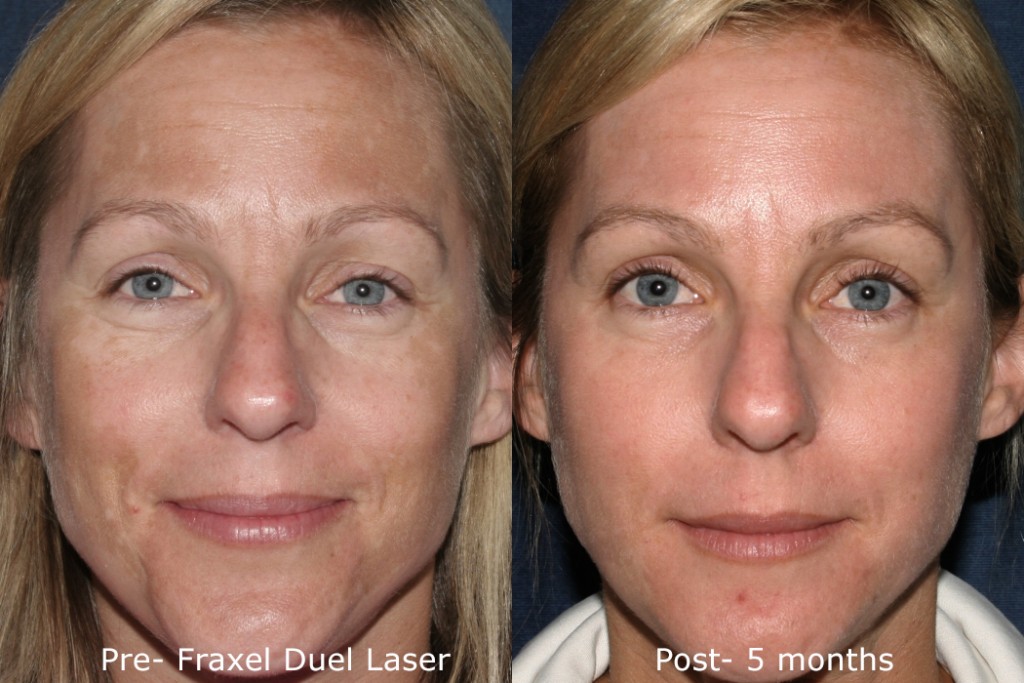
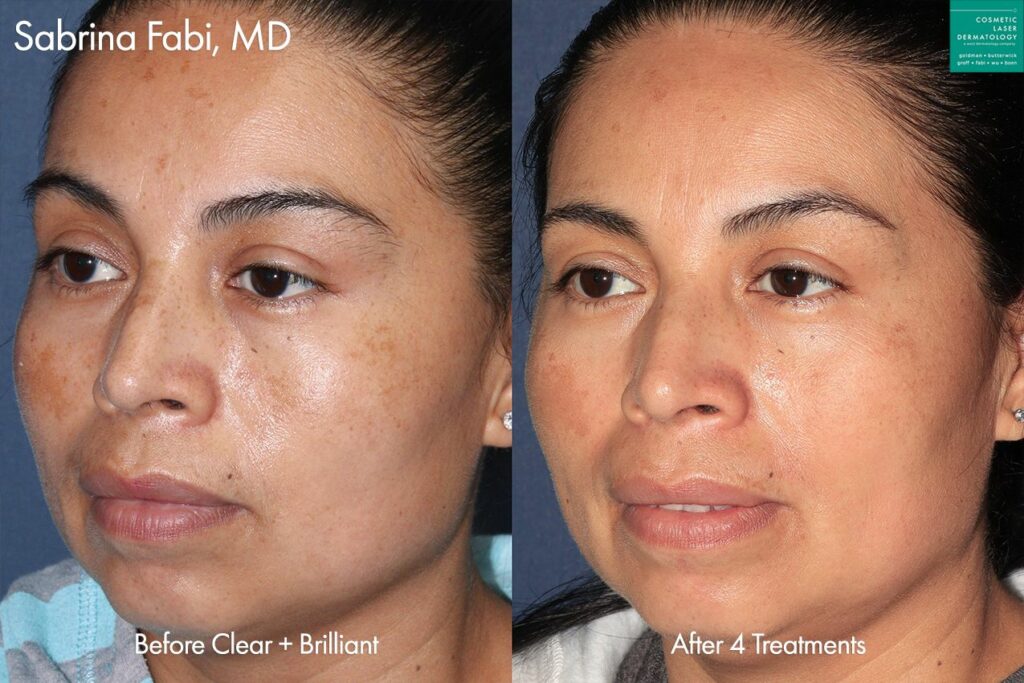
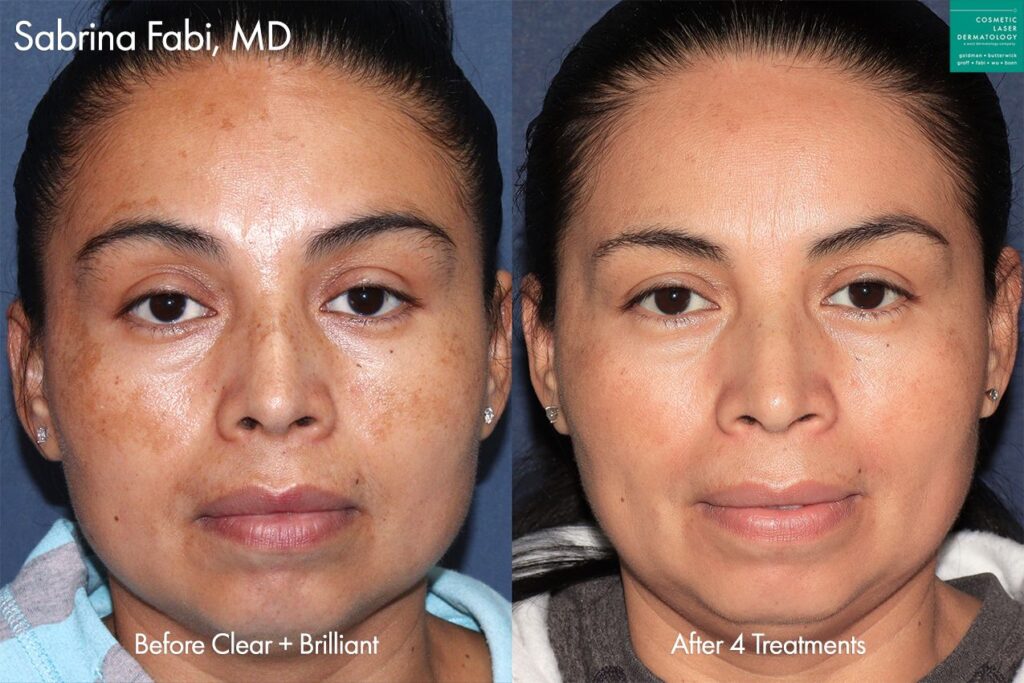
While some cases of chloasma clear up on their own after pregnancy, treatment by a dermatologist may be necessary to lighten and clear up excessive melanin spots on the body. The skincare specialists at Cosmetic Laser Dermatology offer a range of state of the art laser melasma treatments designed to repair sun damage and create a smooth, even skin texture and tone. Cosmetic laser treatments also correct skin damage from sun exposure, which can also increase the risk of developing fine lines, wrinkles, and dry skin.
Aesthetic treatments like chemical peels can also lighten excessive pigmentation and improve skin tone. Schedule a consultation with a dermatologist in San Diego to learn more about:
Laser skin resurfacing and microdermabrasion treatments, such as Dermasweep, are also used for sunspots. Even with proper precautions men and women who live in sunny, warm climates are more susceptible to UV ray exposure. There is a broad range of treatments available for treating sun damage. Laser treatments for sun damage are non-invasive and can help to reverse the early signs of premature aging and spots. medlineplus.gov has more information on treatment options. A consultation with a skilled dermatologist will help to find the treatment method that is right for you.
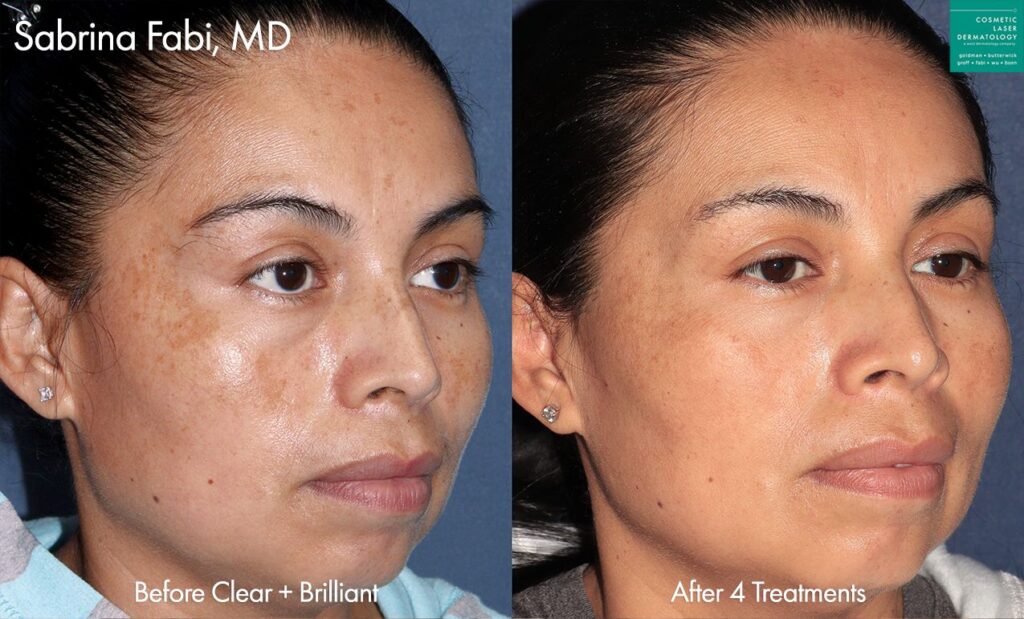
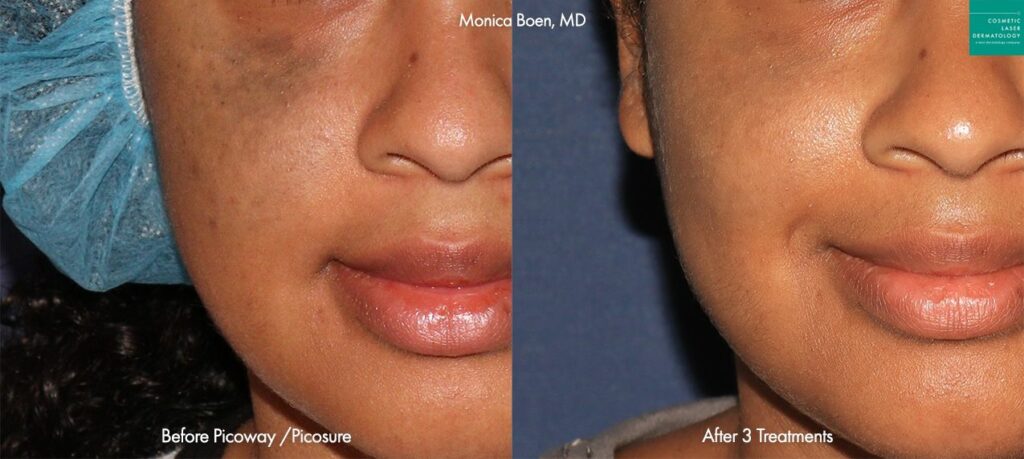
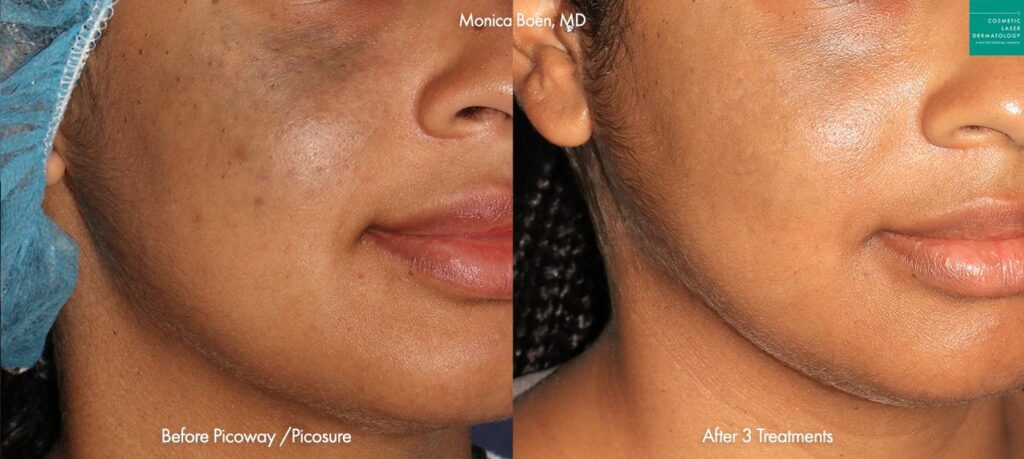
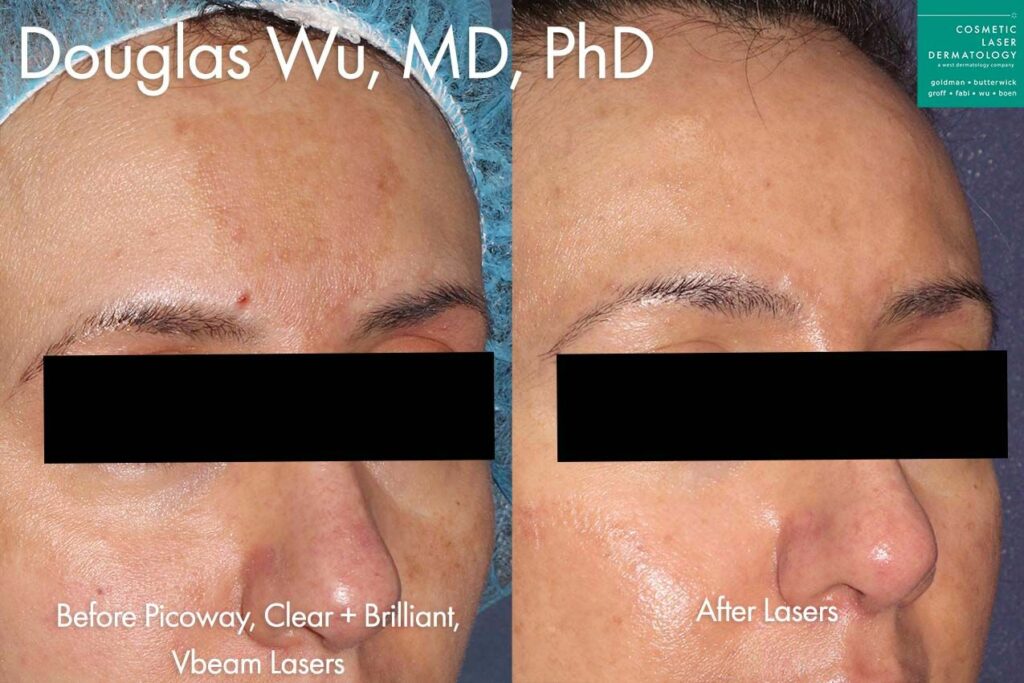
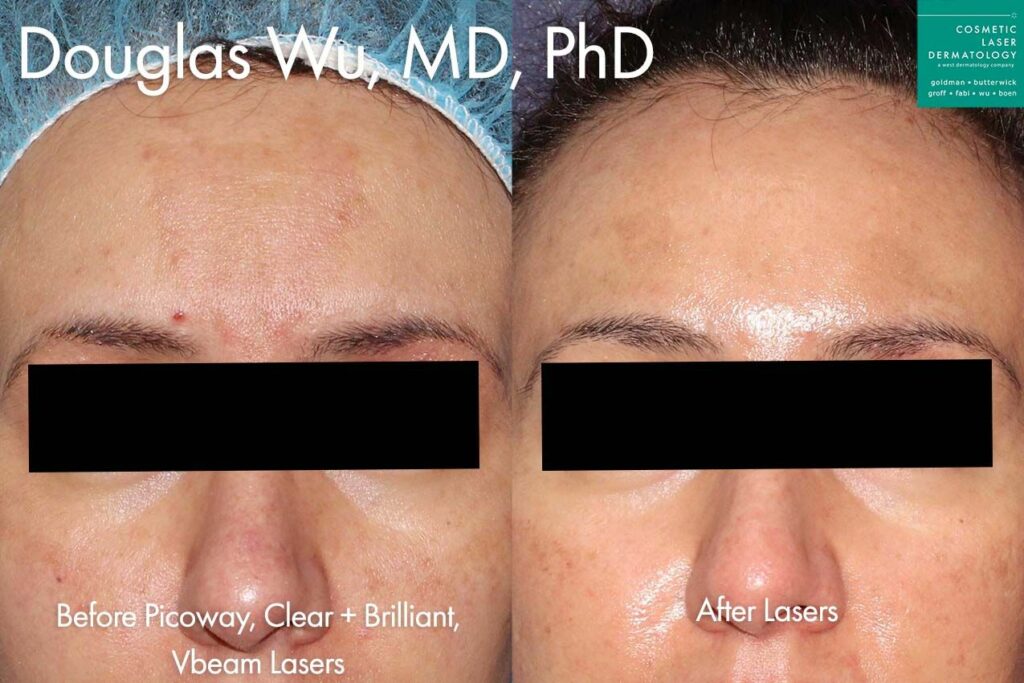
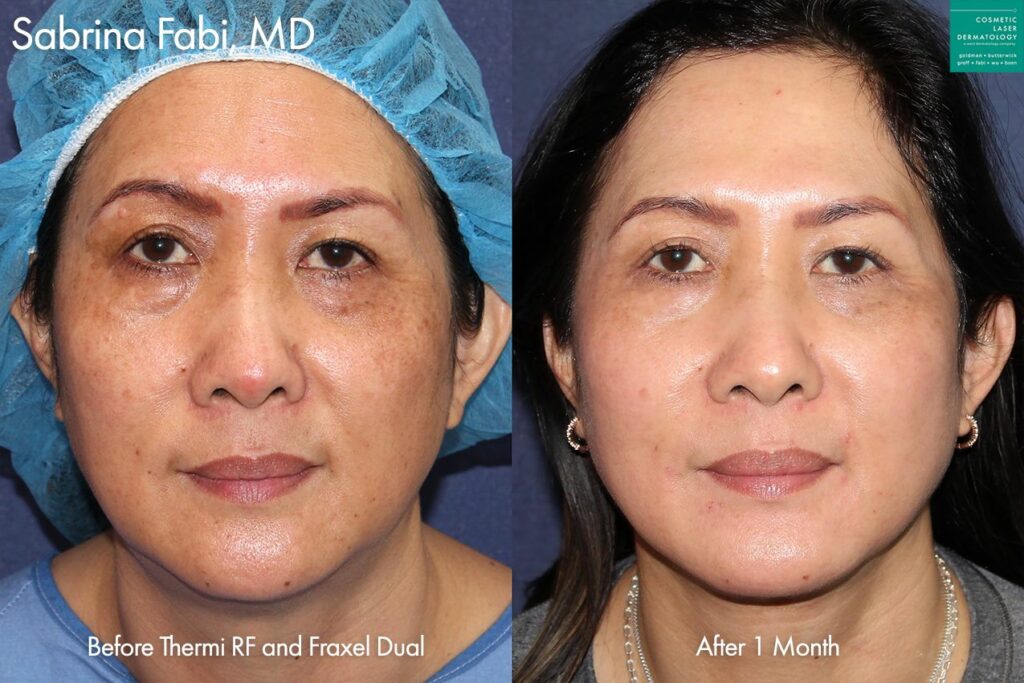
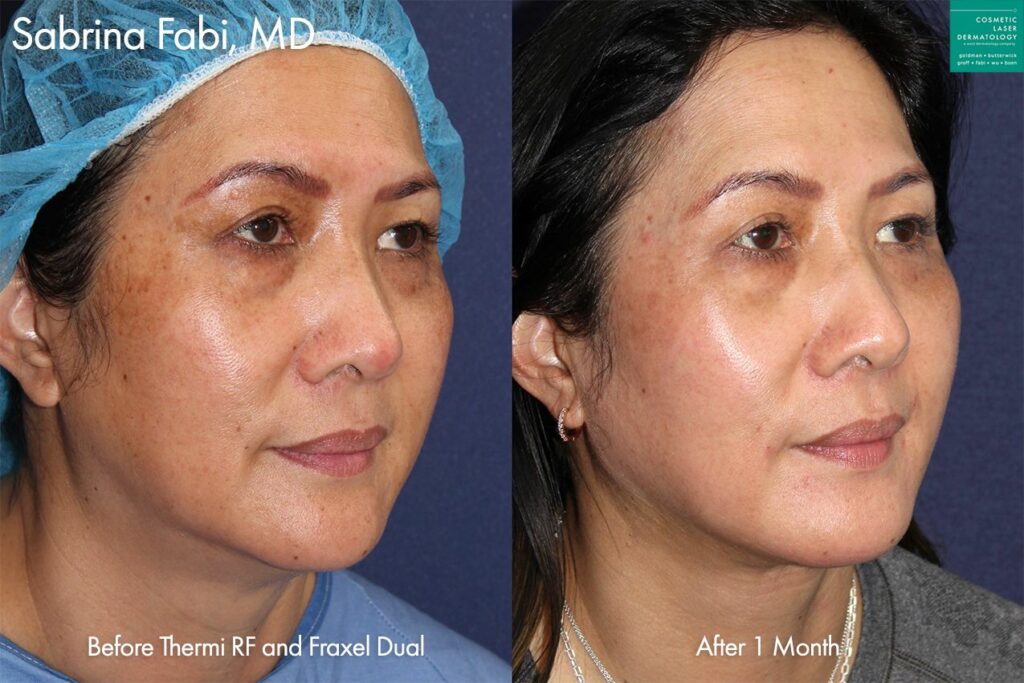
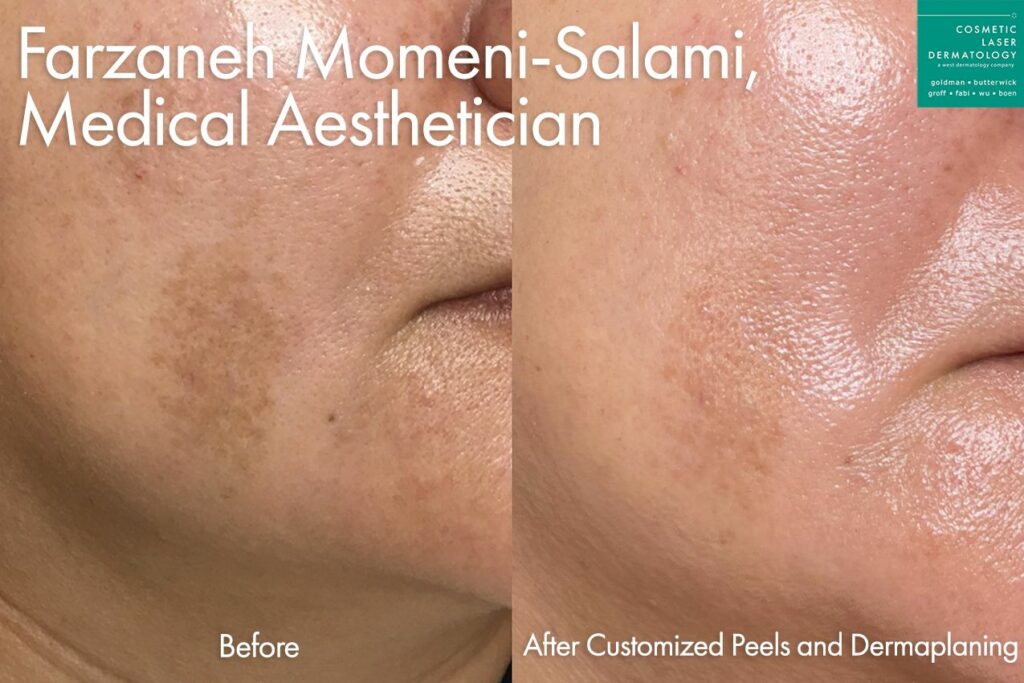
Photos
FAQs
Q: What causes melasma?
The two main causes of melasma are hormonal surges (it is referred to as chloasma when caused by pregnancy) and prolonged sun exposure. Women taking birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy are also at a higher risk of developing melasma. The hormonal surges common during menopause can also increase the risk of developing melasma. An overabundance of the female hormones estrogen and progesterone are believed to overstimulate the melanocytes, which are the cells in the epidermis responsible for producing melanin. Women with tan/light brown skin living in predominantly sunny climates are the most susceptible to the facial hyperpigmentation.
Q: Is melasma dangerous?
Hyperpigmentation from melasma does not pose a risk to the skin or general health. However, prolonged exposure to the sun’s UV rays can cause premature aging and wrinkles, and increase the risk of skin cancer. In rare cases, dark facial patches can also be a symptom of underlying health problems like thyroid disease or Addison’s Disease (Melasma Suprarenale). Although the spots and pigmentation caused by melasma are typically distinguishable from the signs of skin cancer, scheduling regular check-ups with a dermatologist is important to monitor for changes or abnormalities from new or existing moles. Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer in the United States but is highly treatable when diagnosed in the early stages.
Q: Can facial hyperpigmentation be prevented?
When caused by hormonal imbalances from birth control pills, hormone therapy, or as a side effect of certain medications, adjustments can usually be made to the dosage. Because melasma is also caused by sun exposure, protecting the skin from UV rays is the best way to prevent pigmentation and skin cancer. Dermatologists recommend regularly applying a sunscreen of at least 30 with broad-spectrum protection, reapplying every two hours while outdoors for prolonged periods. Protective clothing, sunglasses, and wide-brimmed hands are also important for protection, in addition to sunscreen.